
Deploy RabbitMQ on KubeSphere
RabbitMQ is the most widely deployed open-source message broker. It is lightweight and easy to deploy on premises and in the cloud. It supports multiple messaging protocols. RabbitMQ can be deployed in distributed and federated configurations to meet high-scale, high-availability requirements.
This tutorial walks you through an example of how to deploy RabbitMQ from the App Store of KubeSphere.
Prerequisites
- Please make sure you enable the OpenPitrix system.
- You need to create a workspace, a project, and a user account for this tutorial. The account needs to be a platform regular user and to be invited as the project operator with the
operatorrole. In this tutorial, you log in asproject-regularand work in the projectdemo-projectin the workspacedemo-workspace. For more information, see Create Workspaces, Projects, Users and Roles.
Hands-on Lab
Step 1: Deploy RabbitMQ from the App Store
-
On the Overview page of the project
demo-project, click App Store in the top-left corner. -
Find RabbitMQ and click Install on the App Information page.
-
Set a name and select an app version. Make sure RabbitMQ is deployed in
demo-projectand click Next. -
In App Settings, you can use the default settings directly or customize the settings either by specifying fields in a form or editing the YAML file. Record the value of Root Username and the value of Root Password, which will be used later for login. Click Install to continue.
Tip
To see the manifest file, toggle the Edit YAML switch. -
Wait until RabbitMQ is up and running.
Step 2: Access the RabbitMQ dashboard
To access RabbitMQ outside the cluster, you need to expose the app through a NodePort first.
-
Go to Services and click the service name of RabbitMQ.
-
Click More and select Edit External Access from the drop-down list.
-
Select NodePort for Access Method and click OK. For more information, see Project Gateway.
-
Under Ports, you can see ports are exposed.
-
Access RabbitMQ management through
<NodeIP>:<NodePort>. Note that the username and password are those you set in Step 1.
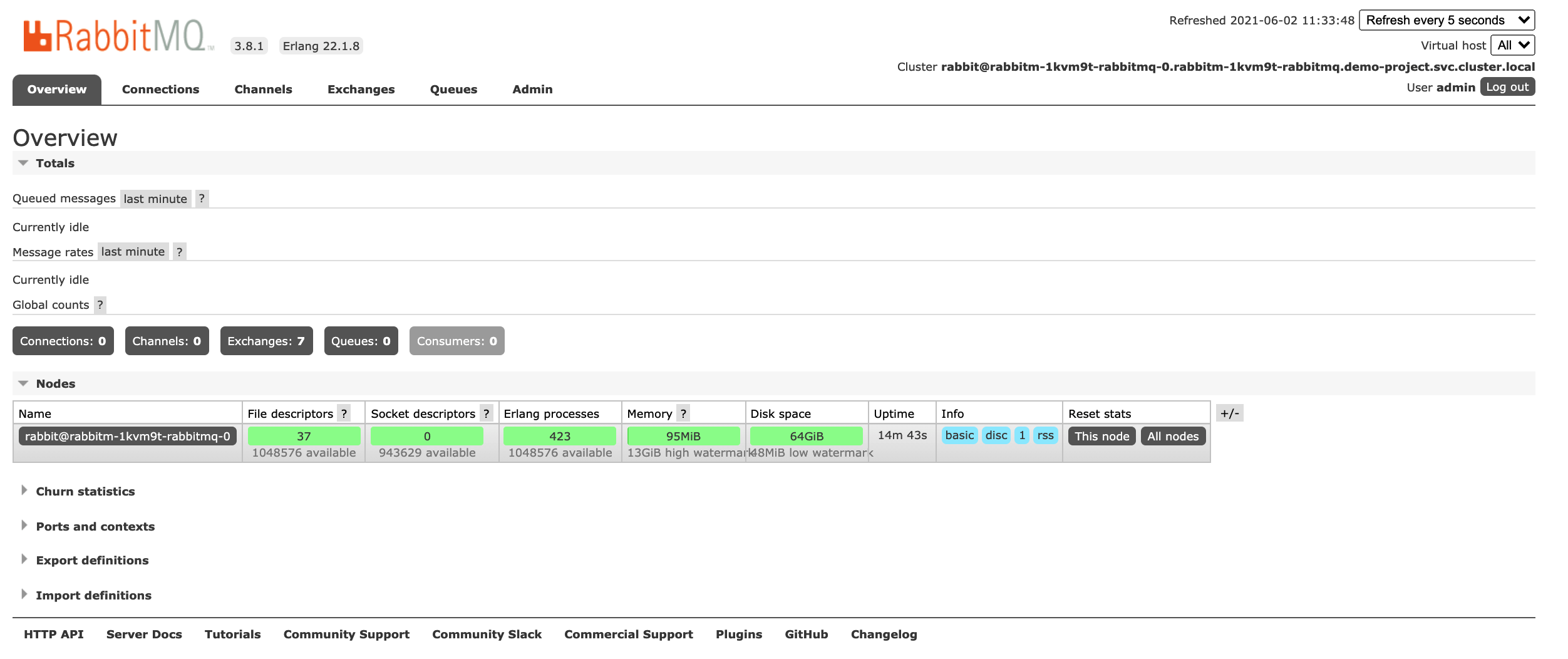
Note
You may need to open the port in your security groups and configure related port forwarding rules depending on where your Kubernetes cluster is deployed. -
For more information about RabbitMQ, refer to the official documentation of RabbitMQ.
Feedback
Was this page Helpful?
Receive the latest news, articles and updates from KubeSphere
Thanks for the feedback. If you have a specific question about how to use KubeSphere, ask it on Slack. Open an issue in the GitHub repo if you want to report a problem or suggest an improvement.












 Previous
Previous
